Virtual Reality (VR) is a technology that is currently still in its infancy. Most forms of VR that are now available to the average consumer have only been publicly accessible for about four years. Due to the novelty of VR, most people are not exactly familiar with its functions, the technology behind it, and its potential real-life application.
VR is a simulated experience that attempts to immerse a user in a completely computer-generated environment. This is most commonly done through the use of headsets and controllers that are being tracked in real time allowing one to not only see a virtual world in 3D, but also to move around, and interact with objects within that virtual space.
Currently, the most popular and well-known use of VR is in entertainment. This can range from video games that allow for full immersion, to movies and videos shot using 360-degree cameras placing the viewer right in the action. In addition to that there are also other forms of VR, such as Augmented Reality (AR), which adds digital elements on top of a real-world environment in order to enhance what we see, and Mixed Reality (MR), which combines elements of VR and AR so that physical objects in the real world interact with digital objects. Companies and independent business are also prototyping and experimenting with a variety of ideas, such as gloves that provide haptic feedback allowing the user to actually feel virtual objects and their texture, or treadmills that allow you to comfortably walk and run around in an environment without needing to worry that you will hit a wall in real-life.
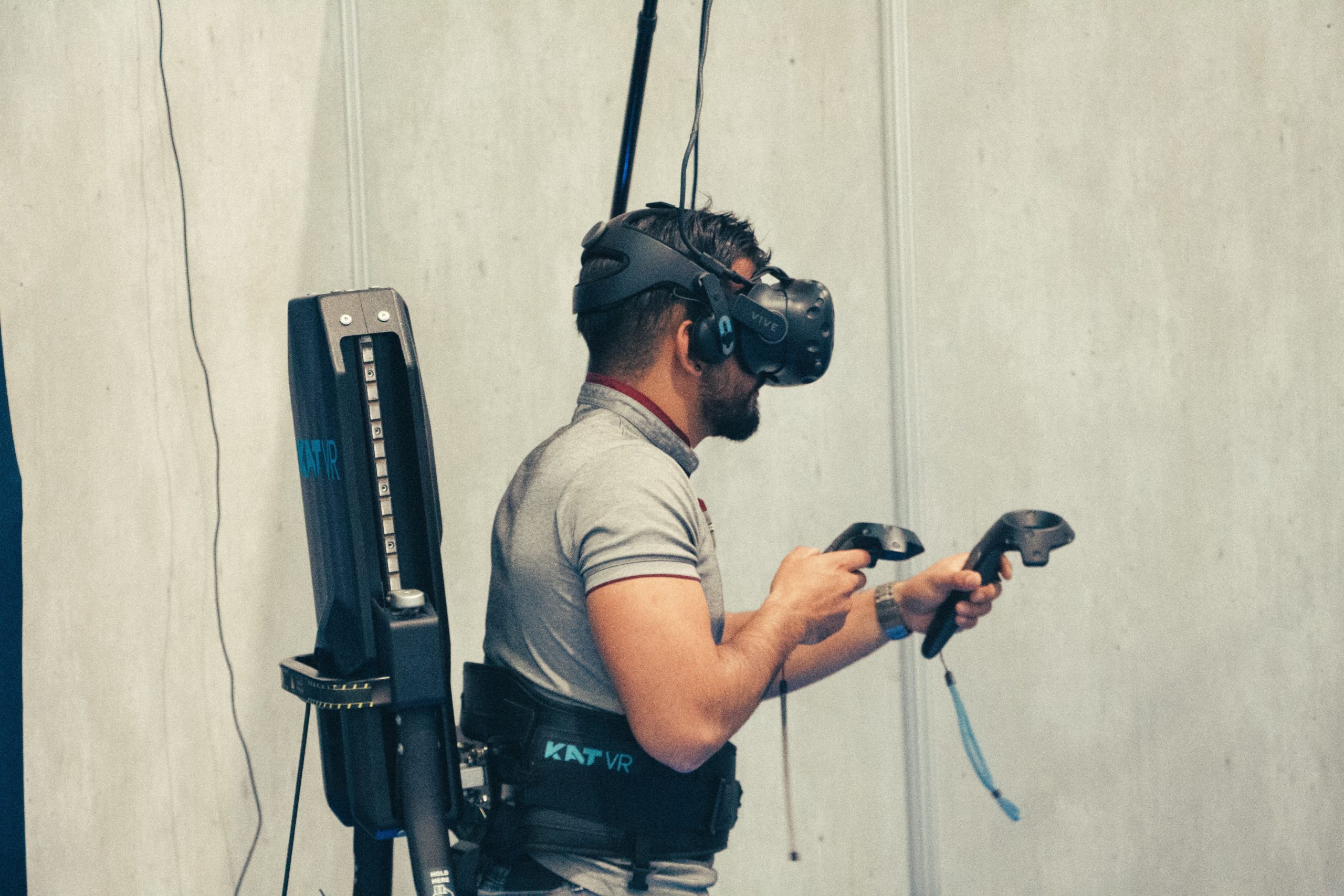

However, one use that is becoming more popular and potentially more important due to its real-life application is VR’s use in education and training. Due to the sheer limitless possibilities that VR provides it can not only provide entertainment to people, but it can also be used to simulate scenarios that would otherwise be too dangerous, too expensive, or even completely impossible to create without VR. For example, in medical school they can use the different forms of VR to teach anatomy. Students are able to see a 3D model of the human body and can manipulate it and dissect it. This allows them to get a clear view of bodily functions without needing to either dissect physical bodies, or work with real models that might lack the same level of interactivity. In addition to that, it can save money as trying to get a cadaver to dissect can be pricey and is not as easy to come by as a virtual one. Furthermore, it can also be used to train surgeons, allowing them to get familiar with the operation procedure in a safe and controlled environment whilst still maintaining a high level of realism.
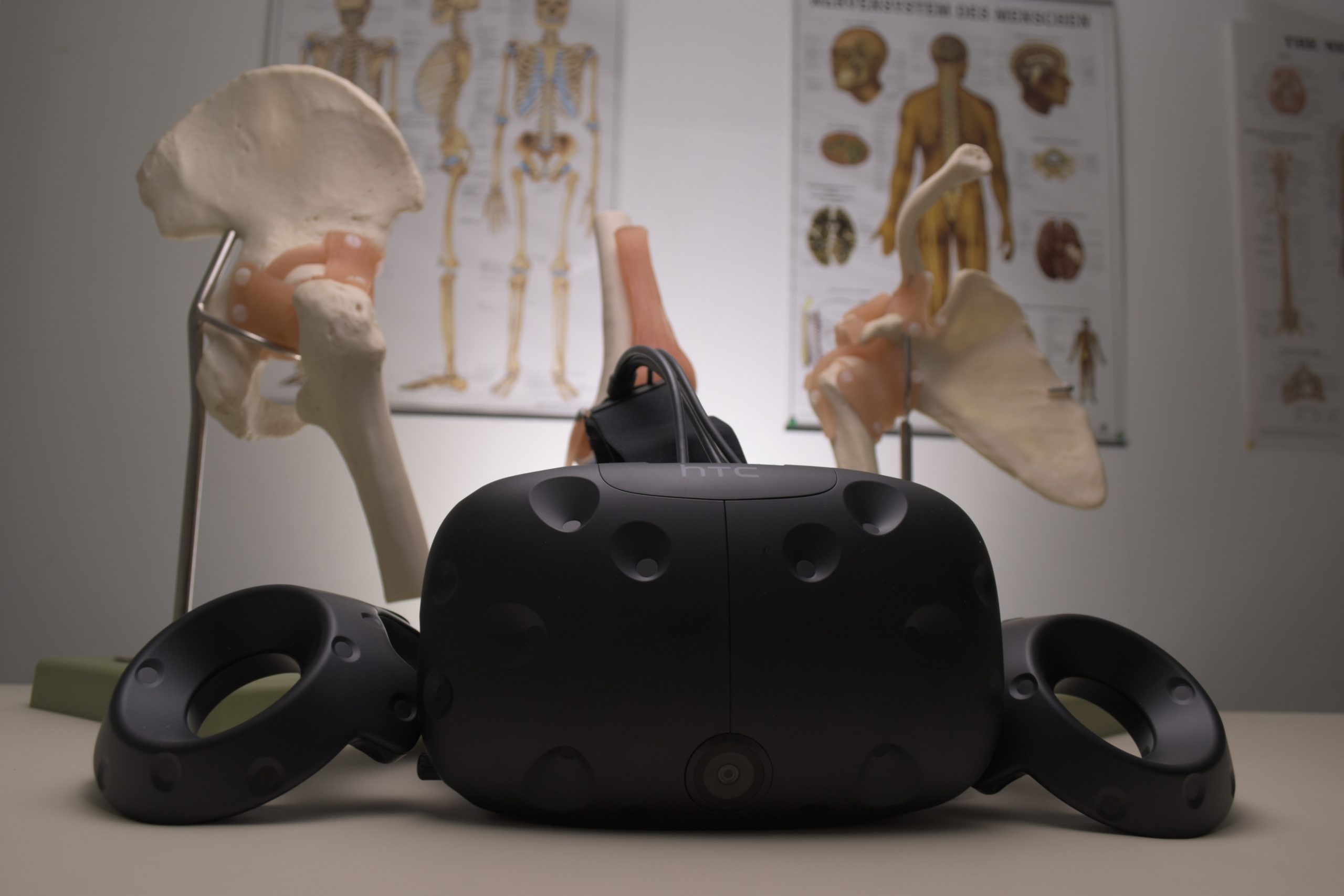
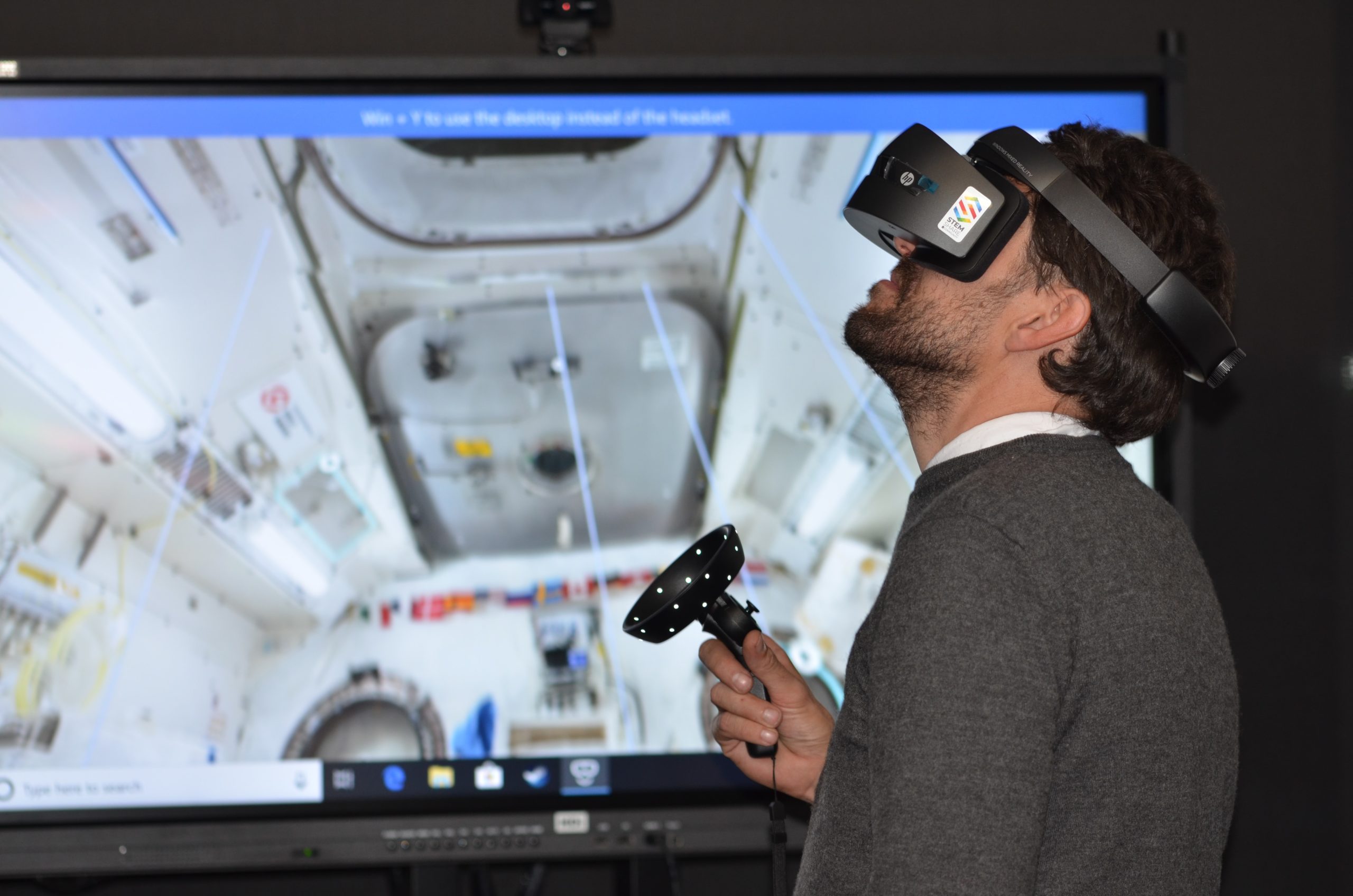


On the other hand, VR can also be used in high schools. According to Paula Dias Leite, a professor at Webster University Geneva, who is currently working on a PhD in VR/AR/MR Story Telling, schools began using this technology in order to “engage students in subjects that they might not be interested in”. She has seen VR being used in science classes to show students the concepts that they are studying. For example, in a chemistry class they could enter VR and look at different molecules and elements to see their makeup, and how they might bond with others. This can help the students make sense of what they are studying as visualizing it in an interactive environment can help reinforce what they see in class and in their textbooks. However, there are some issues that could arise when using VR. Leite said that one main concern when using VR is that it has a tendency of making people motion sick. This is mainly caused by a disconnect between what is being seen, and what the rest of the body perceives. A sense of discomfort and nausea is more common in younger people as their bodies are still developing, therefore experts advise against the use of VR for people under the age of 20.
Overall, VR is still undergoing heavy development as it has not been around for a long time. There are still new devices and technologies that are being worked on in order to improve the overall user-experience. Virtual Reality is the most immersive technology available at the moment, allowing users to experience almost anything, anywhere, and at any time. As the technology becomes more sophisticated the amount of possible applications can only increase.